Mapping the Opioid Crisis: A Deep Dive into Overdose Data from Q2 2023
Bottom line up front: Fentanyl is showing up as a major problem in emergency rooms and OD’s. This Q2 report will help you understand the other drugs mixed with fentanyl that are showing up so you can stay ahead of the curve.
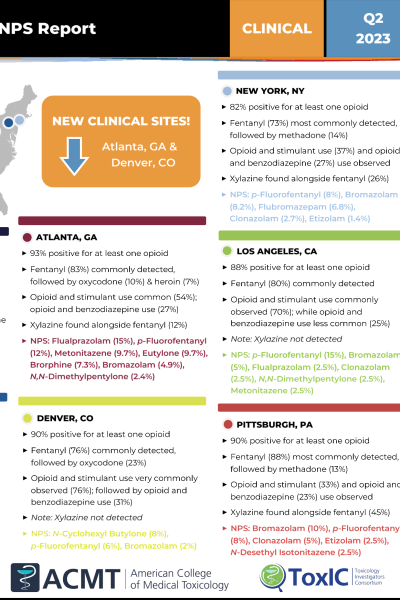
ToxIC Fentalog Study Group: Synthetic Opioid Prevalence in U.S. Cities – Q2 2023
In an effort to better understand and address the opioid crisis in the United States, the ToxIC Fentalog Study Group – a collaboration between the American College of Medical Toxicology and the Center for Forensic Science Research and Education – has issued their Q2 2023 report. It provides an overview of the prevalence and types of synthetic opioids and other drugs involved in suspected overdose cases across various U.S. cities.
A Comprehensive Approach to Overdose Investigation
The study's methodology involved collecting residual, discarded biological samples from suspected opioid overdose patients presenting to emergency departments. These samples were then tested against an expansive library of drugs and other substances. The data gives a real-time assessment of the current drug market and its implications for clinical institutions.
Key Findings: Opioid Prevalence
The study revealed high levels of opioid prevalence in every tested city. Rates of positive tests for at least one opioid ranged from 75% in Bethlehem, PA, to a startling 100% in Portland, OR.
Fentanyl: A Consistent Threat
Fentanyl was the most commonly detected drug across all cities, with prevalence rates ranging from 56% in Portland, OR, to 88% in Pittsburgh, PA. Its potent effects and widespread availability contribute to its status as a persistent threat in the ongoing opioid crisis.
Polydrug Use: A Complicated Problem
The study also identified a significant amount of polydrug use, with concurrent opioid and stimulant use observed across the board, ranging from 25% in Bethlehem, PA, to 76% in Denver, CO. Concurrent opioid and benzodiazepine use was also noted, with rates between 23% and 44%.
The Presence of Xylazine and Novel Psychoactive Substances
In some cities, xylazine, a veterinary sedative, was detected alongside fentanyl. A variety of Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPS), including but not limited to Clonazolam, Flualprazolam, p-Fluorofentanyl, Metonitazene, Eutylone, and Bromazolam, were also detected across the cities.
Implications and Next Steps
These findings provide valuable insights for clinicians, researchers, and policymakers. The prevalence and variety of substances detected in this study highlight the complexity of the drug market and the challenges faced by those seeking to treat and prevent overdoses. It underscores the need for a multi-faceted approach in addressing the ongoing opioid crisis, including comprehensive drug testing, targeted treatment strategies, and effective harm reduction efforts.
With this current snapshot of the drug market, the healthcare community and relevant stakeholders can be better equipped to respond to this persistent and evolving crisis. Future reports will continue to track these trends, contributing to our collective understanding and ability to respond to this complex and urgent issue.